Debt-to-GDP Ratio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

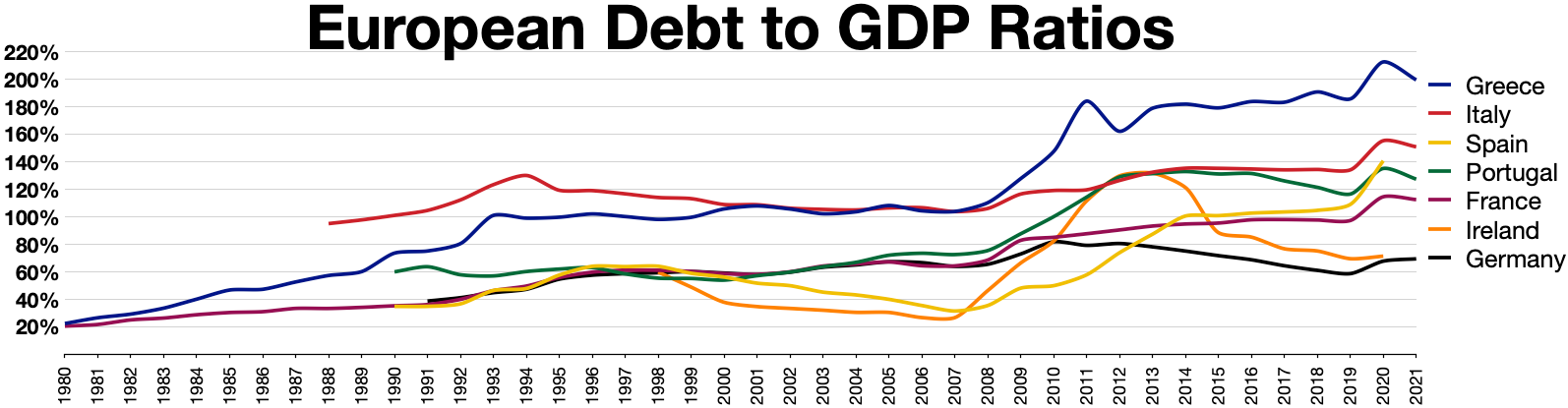 At the end of the 1st quarter of 2021, the
At the end of the 1st quarter of 2021, the
Federal Bank of St. Louis. According to the IMF World Economic Outlook Database (April 2021),International Monetary Fund
World Economic Outlook Database''General government gross debt''(Percent of GDP)
the level of Gross Government debt-to-GDP ratio in Canada was 116.3%, in China 66.8%, in India 89.6%, in Germany 70.3%, in France 115.2% and in the United States 132.8%. Two-thirds of US public debt is owned by US citizens, banks, corporations, and the
economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and intera ...
, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
between a country's government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
(measured in units of currency) and its gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). While it is a "ratio", it is technically measured in units of year, and can be interpreted as the number of years a country needs to pay off its entire debt, if all its GDP is devoted towards it. A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates that an economy produces goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt. Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
, war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
, recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
s, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
.
It should not be confused with a deficit-to-GDP ratio, which, for countries running budget deficits, measures a country's annual net fiscal loss in a given year ( total expenditures minus total revenue, or the net change in debt per annum) as a percentage share of that country's GDP; for countries running budget surpluses, a ''surplus-to-GDP ratio'' measures a country's annual net fiscal ''gain'' as a share of that country's GDP.
Particularly in macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
, various debt-to-GDP ratios can be calculated. The most commonly used ratio is the government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
divided by the gross domestic product (GDP), which reflects the government's finances, while another common ratio is the total debt to GDP, which reflects the finances of the nation as a whole.
Changes
The change in debt-to-GDP is approximately "net change in debt as percentage of GDP"; for government debt, this is deficit or ( surplus) as percentage of GDP. This is only approximate as GDP changes from year to year, but generally, year-on-year GDP changes are small (say, 3%), and thus this is approximately correct. However, in the presence of significantinflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
, or particularly hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as t ...
, GDP may increase rapidly in nominal terms; if debt is nominal, then its ratio to GDP will decrease rapidly. A period of deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% (a negative inflation rate). Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflation ...
would have the opposite effect.
A government's debt-to-GDP ratio can be analysed by looking at how it changes or, in other words, how the debt is evolving over time:
The left hand side of the equation demonstrates the dynamics of the government's debt. is the debt-to-GDP at the end of the period , and is the debt-to-GDP ratio at the end of the previous period (−1). Hence, the left side of the equation shows the ''change'' in the debt-to-GDP ratio. The right hand side of the equation shows the causes of the government's debt. is the interest payments on the stock of debt as a ratio of GDP so far, and shows the primary deficit-to-GDP ratio.
If the government has the ability to print money, and therefore monetize
Monetization (American and British English spelling differences, also spelled monetisation) is, broadly speaking, the process of converting something into money. The term has a broad range of uses. In banking, the term refers to the process of co ...
the outstanding debt, the budget constraint becomes:
The term is the change in money balances (i.e. money growth). By printing money the government is able to increase nominal money balances to pay off the debt (consequently acting in the debt way that debt financing does, in order to balance the government's expenditures). However, the effect that an increase in nominal money balances has on seignorage
Seigniorage , also spelled seignorage or seigneurage (from the Old French ''seigneuriage'', "right of the lord (''seigneur'') to mint money"), is the difference between the value of money and the cost to produce and distribute it. The term can be ...
is ambiguous, as while it increases the amount of money within the economy, the real value of each unit of money decreases due to inflationary effects. This inflationary effect from money printing is called an inflation tax
Seigniorage , also spelled seignorage or seigneurage (from the Old French ''seigneuriage'', "right of the lord (''seigneur'') to mint money"), is the difference between the value of money and the cost to produce and distribute it. The term can be ...
.
Applications
Debt-to-GDP measures thefinancial leverage
In finance, leverage (or gearing in the United Kingdom and Australia) is any technique involving borrowing funds to buy things, hoping that future profits will be many times more than the cost of borrowing. This technique is named after a lever ...
of an economy.
One of the Euro convergence criteria
The euro convergence criteria (also known as the Maastricht criteria) are the criteria which European Union member states are required to meet to enter the third stage of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) and adopt the euro as their currenc ...
was that government debt-to-GDP should be below 60%.
The World Bank and the IMF hold that "a country can be said to achieve external debt sustainability if it can meet its current and future external debt service obligations in full, without recourse to debt rescheduling or the accumulation of arrears and without compromising growth". According to these two institutions, external debt sustainability can be obtained by a country "by bringing the net present value (NPV) of external public debt down to about 150 percent of a country's exports or 250 percent of a country's revenues". High external debt is believed to have harmful effects on an economy. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 17
Sustainable Development Goal 17 (SDG 17 or Global Goal 17) is about "partnerships for the goals." One of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, the official wording is: "Strengthen the means of implemen ...
, an integral part of the 2030 Agenda has a target to address the external debt of highly indebted poor countries to reduce debt distress.
In 2013 Herndon
Herndon may refer to:
People
* Herndon (surname), an American surname
* Herndon Davis (1901–1962), American artist, journalist, illustrator, and painter
Places in the United States Communities
* Herndon, California, an unincorporated commun ...
, Ash, and Pollin reviewed an influential, widely cited research paper entitled, "Growth in a Time of Debt
''Growth in a Time of Debt'', also known by its authors' names as Reinhart–Rogoff, is an economics paper by American economists Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff published in a non peer-reviewed issue of the ''American Economic Review'' in 2010. ...
", by two Harvard economists Carmen Reinhart
Carmen M. Reinhart (née Castellanos, born October 7, 1955) is a Cuban-American economist and the Minos A. Zombanakis Professor of the International Financial System at Harvard Kennedy School. Previously, she was the Dennis Weatherstone Senior Fe ...
and Kenneth Rogoff
Kenneth Saul Rogoff (born March 22, 1953) is an American economist and chess Grandmaster. He is the Thomas D. Cabot Professor of Public Policy and professor of economics at Harvard University.
Early life
Rogoff grew up in Rochester, New York. ...
. Herndon, Ash and Pollin argued that "coding errors, selective exclusion of available data, and unconventional weighting of summary statistics lead to serious errors that inaccurately represent the relationship between public debt and GDP growth among 20 advanced economies in the post-war period". Correcting these basic computational errors undermined the central claim of the book that too much debt causes recession. Rogoff and Reinhardt claimed that their fundamental conclusions were accurate, despite the errors.
There is a difference between external debt denominated in domestic currency, and external debt denominated in foreign currency. A nation can service external debt denominated in domestic currency by tax revenues, but to service foreign currency debt it has to convert tax revenues in the foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspec ...
to foreign currency, which puts downward pressure on the value of its currency.
Global statistics

 At the end of the 1st quarter of 2021, the
At the end of the 1st quarter of 2021, the United States public debt
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury sec ...
-to-GDP ratio was 127.5%.Federal Debt: Total Public Debt as Percent of Gross Domestic ProductFederal Bank of St. Louis. According to the IMF World Economic Outlook Database (April 2021),International Monetary Fund
World Economic Outlook Database''General government gross debt''(Percent of GDP)
the level of Gross Government debt-to-GDP ratio in Canada was 116.3%, in China 66.8%, in India 89.6%, in Germany 70.3%, in France 115.2% and in the United States 132.8%. Two-thirds of US public debt is owned by US citizens, banks, corporations, and the
Federal Reserve Bank
A Federal Reserve Bank is a regional bank of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. There are twelve in total, one for each of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts that were created by the Federal Reserve A ...
;
approximately one-third of US public debt is held by foreign countries – particularly China and Japan. In comparison, less than 5% of Italian and Japanese public debt is held by foreign countries.
See also
*Economic bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be c ...
* Debt levels and flows
* Leverage (finance)
In finance, leverage (or gearing in the United Kingdom and Australia) is any technique involving borrowing funds to buy things, hoping that future profits will be many times more than the cost of borrowing. This technique is named after a lever i ...
* List of countries by public debt
Below is a list of countries and territories by government debt , public debt (also called government debt or sovereign debt). ''Gross'' government debt is government financial liabilities that are debt instruments. A ''debt instrument'' is a f ...
* List of countries by external debt
This is a list of countries by external debt, it is the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods or services, where the public debt is the money or credit owed by any level of gov ...
* List of sovereign states by tax revenue to GDP ratio
This article lists countries alphabetically, with total tax revenue as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) for the listed countries. The tax percentage for each country listed in the source has been added to the chart.
Tax as ...
References
{{Reflist Debt-to-GDP ratio